The essential 8 are cyber security controls that make it harder for criminals to access computer systems.
We encourage your business use these strategies to help mitigate your risk of cyber attack.
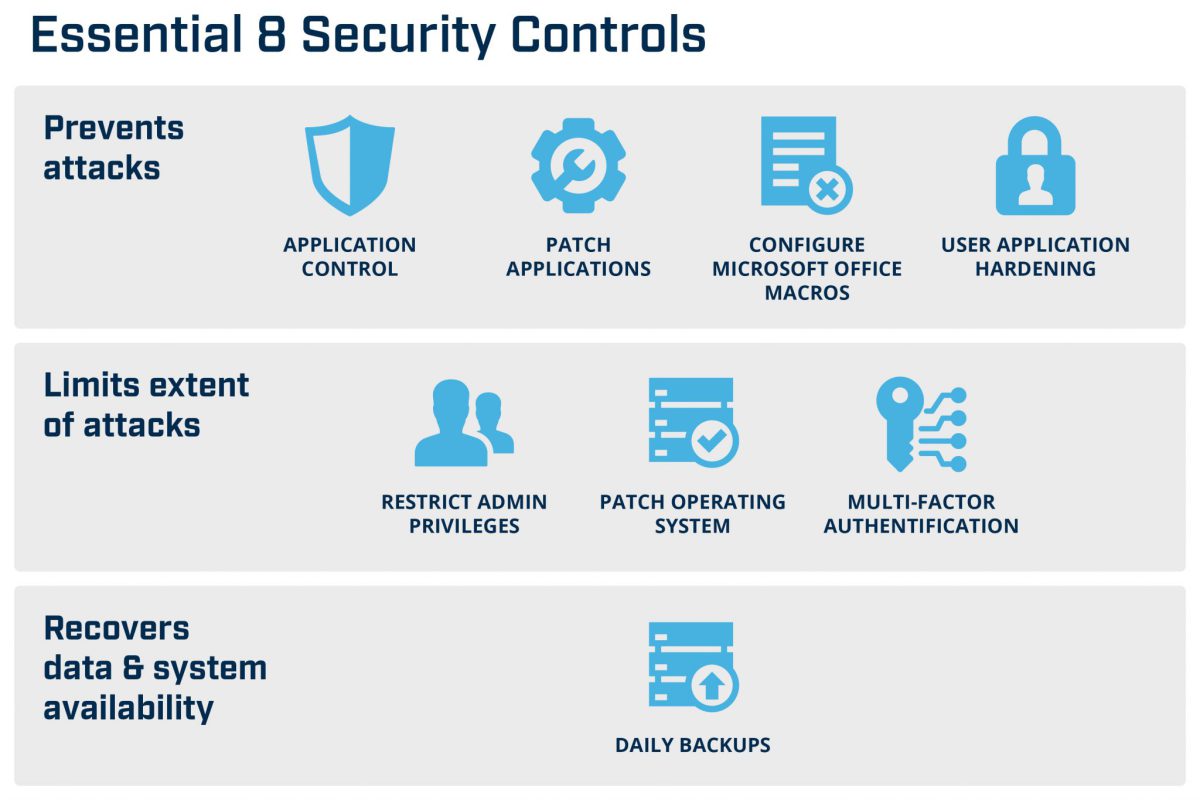
Strategies to Help Prevent Malware
1. Application control – Prevent the execution of malicious programs including .exe, DLL, scripts (e.g. Windows Script Host, PowerShell and installers).
Why: Malicious code is often contained in non-approved applications. Blocking these type of applications will prevent them running and infecting your systems.
2. Patch applications – Adobe, Microsoft Office, Java and PDF viewers etc. Attempt to patch high risk vulnerabilities within 48 hours of patch release. Always update and use the latest version of applications.
Why: Security vulnerabilities in software applications are often exploited to run malicious code.
3. Application hardening – Configure web browsers to block Flash (ideally uninstall it), ads, and Java. Disable features that are not used or required in Microsoft Office (e.g. OLE), web browsers and other applications, such as PDF viewers.
Why: Flash, ads and Java are common ways to deliver and execute malicious code.
4. Configure Microsoft Office macro settings – Block macros from the internet and only allow vetted macros in ‘trusted locations’ with limited write access or use digitally signed trusted certificates.
Why: Microsoft Office macros are often used to deliver and execute malicious code.
Strategies to Mitigate the risk of Cyber Security Attacks
5. Multi-factor authentication – Enable MFA for all users (where possible) to protect your online services, RDP, VPNs, SSH and other remote access methods.
Why: Multi-factor user authentication makes it harder to access online systems.
6. Patch operating systems – Patch all systems (computer and network devices) with high risk vulnerabilities as soon as possible. Always update to the latest operating system version and never use unsupported versions.
Why: Software vulnerabilities are often used to infiltrate devices
7. Restrict administrative privileges – Don’t allow users to use privileged user accounts on operating systems and applications. Validate the need for privileges based on user requirements.
Why: Administrator accounts have full access to everything. Restricting their use reduces the risk of them being hijacked or compromised.
Strategies to Recover Data and System Availability
8. Daily backups – Ensure new and modified data including software and configuration settings are backed up daily. Ideally retain, disconnected or offline for 3 three months. Regularly test restores should be performed.
Why: Ensures data and systems can be recovered following a cyber security incident.
The essential 8 small business cyber security tips are globally recognised as key strategies in the fight against cyber crime.
These baseline security methods are advised by the National Cyber Security Centre and the Australian Cyber Security Centre.
To help further protect your organisation against cyber attacks, we recommend completing a Cyber Essentials certification.
For more information on how you can improve your cyber security, book your free Fentons IT consultation with one of our experts.